Smart Contracts: Revolutionizing Digital Agreements Today
Understanding Smart Contracts: The Future of Digital Agreements
What Are Smart Contracts and How Do They Work?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They reside on a blockchain, making them immutable and transparent. These digital contracts automatically enforce and execute the terms when predetermined conditions are met. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces the risk of disputes or fraud.
The essential components of smart contracts include the blockchain platform, programming language, and the conditions for execution. Most smart contracts are built on platforms like Ethereum, which allows developers to create complex agreements using languages like Solidity. Once deployed, these contracts can be interacted with through blockchain transactions, triggering actions such as fund transfers or data sharing.
One of the significant advantages of smart contracts is their ability to operate autonomously. When the conditions specified in the code are met, the contract executes itself without human intervention. For instance, in a supply chain scenario, once goods are delivered and confirmed by the parties involved, payment is automatically released to the supplier.
Overall, smart contracts represent a paradigm shift in how agreements are formed and enforced. They promise efficiency and reliability but require a robust understanding of the legal and technological frameworks that underpin them.
The Rise of Blockchain Technology in Digital Agreements
Blockchain technology serves as the backbone of smart contracts, providing a decentralized, secure, and transparent environment for digital agreements. Its distributed ledger system ensures that once information is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted without consensus from the network. This feature makes blockchain particularly appealing for industries where trust and verification are paramount.
The adoption of blockchain technology is rapidly increasing across various sectors, such as finance, healthcare, real estate, and supply chain management. Companies are leveraging blockchain to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance security. Smart contracts are at the forefront of this revolution, facilitating transactions and agreements that are not only faster but also more reliable.
The rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) has also contributed significantly to the popularity of smart contracts. DeFi platforms utilize smart contracts to automate financial transactions, enabling users to lend, borrow, and trade without relying on traditional banking systems. This shift towards decentralization is changing the landscape of financial agreements, making them more accessible to a broader audience.
As awareness and understanding of blockchain technology grow, so does the potential for smart contracts to redefine digital agreements. The future looks promising as more industries explore innovative ways to integrate these contracts into their operations, leading to enhanced efficiency and transparency.
Key Benefits of Using Smart Contracts in Business
Smart contracts offer several key benefits that make them an attractive option for businesses looking to improve their contractual agreements. First and foremost, they provide increased efficiency. By automating processes, businesses can reduce the time spent on drafting, negotiating, and executing contracts. This efficiency translates into faster transactions and the ability to focus on core business operations.
Another significant advantage is cost reduction. Traditional contracts often involve legal fees, administrative costs, and intermediary expenses. Smart contracts eliminate the need for middlemen, allowing parties to interact directly on the blockchain. This reduction in overhead can lead to significant savings, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Additionally, smart contracts enhance security and trust. The decentralized nature of blockchain makes it nearly impossible for unauthorized parties to alter contract terms. Parties can trust that the agreed-upon conditions will be enforced automatically, reducing the risk of fraud and disputes. Furthermore, the transparency inherent in blockchain technology allows all parties to verify the contract’s execution in real-time.
Finally, smart contracts provide scalability. As businesses grow, so too do their contractual needs. Smart contracts can easily adapt to handle an increasing number of transactions without the complexities associated with traditional contracts. This scalability ensures that as a business expands, its transactional processes remain streamlined and efficient.
Common Misconceptions About Smart Contracts Debunked
Despite the growing popularity of smart contracts, several misconceptions persist that can hinder their adoption. One common myth is that smart contracts are entirely autonomous and do not require any human oversight. While they do execute automatically based on predefined conditions, humans are still responsible for defining those conditions accurately. Errors in programming or misunderstandings of the contract can lead to unintended consequences.
Another prevalent misconception is that smart contracts are entirely irreversible. While it is true that once executed, a smart contract’s actions cannot be undone, it is essential to note that the agreement itself can be designed to include clauses for modifications or terminations. Parties can create flexible smart contracts that allow for certain adjustments in response to changing conditions or needs.
Additionally, many believe that smart contracts are only suitable for cryptocurrency transactions. However, their application extends far beyond financial transactions. Smart contracts can automate a variety of processes, including property transfers, voting systems, and supply chain management, making them versatile tools for many industries.
Finally, some people assume that using smart contracts is inherently complicated and requires extensive technical knowledge. While creating and deploying smart contracts does require some programming skills, numerous user-friendly platforms are emerging that allow non-technical users to create and manage smart contracts with ease. As the technology matures, accessibility is expected to improve, fostering wider adoption.
Legal Implications and Challenges of Smart Contracts
While smart contracts offer numerous advantages, they also bring forth legal implications and challenges that need careful consideration. One of the primary concerns is the lack of standardized regulations governing smart contracts across different jurisdictions. Since these contracts operate on a decentralized network, inconsistencies in legal frameworks can lead to complications when disputes arise.
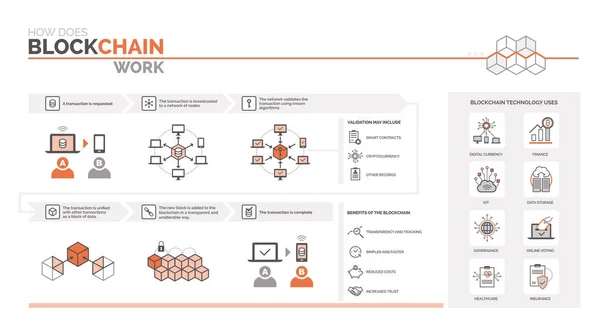
Another legal challenge is the enforceability of smart contracts. While they may be self-executing, their compliance with existing contract law remains a question. Courts may need to determine how to interpret the terms coded into a smart contract, especially in cases where the language is ambiguous or if the conditions do not align with legal standards.
Additionally, issues related to data privacy and security arise when using smart contracts. Sensitive information might be stored on the blockchain, raising concerns about who has access to this data and how it is protected. Businesses must ensure that they comply with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, which can conflict with the immutable nature of blockchain.
Finally, the potential for programming errors poses a significant risk. A flaw in the code can lead to unintended outcomes, including financial losses. As a result, organizations using smart contracts should invest in thorough testing and validation processes to minimize these risks and ensure that their contracts function as intended.
The Future of Smart Contracts: Trends and Predictions
The future of smart contracts looks promising, with several trends and predictions shaping the landscape of digital agreements. One notable trend is the increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with smart contracts. This combination can enhance automation, allowing contracts to adapt to changing conditions and learn from previous transactions, leading to more intelligent and responsive agreements.
Another prediction is the growth of cross-chain interoperability. As various blockchain platforms emerge, the ability for smart contracts to interact across different chains will become crucial. This interoperability will facilitate broader collaboration among businesses and industries, allowing for seamless transactions and agreements regardless of the underlying technology.
Moreover, as regulatory frameworks around blockchain technology evolve, clearer guidelines for smart contracts are likely to emerge. This regulatory clarity will help businesses navigate the legal landscape more confidently, encouraging wider adoption. Governments worldwide are beginning to recognize the potential of blockchain, and as they establish regulations, the legitimacy of smart contracts will be further solidified.
Lastly, the increasing focus on sustainability will influence the development of smart contracts. There is growing awareness of the environmental impact of blockchain technology, particularly concerning energy consumption. Future iterations of smart contracts may prioritize eco-friendly practices, utilizing more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms and promoting sustainability in contract execution.
| Feature | Traditional Contracts | Smart Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Manual | Automated |
| Intermediaries | Often required | Direct peer-to-peer interactions |
| Cost | Higher due to legal fees | Lower due to automation |
| Security | Vulnerable to tampering | Immutable and secure |
| Transparency | Limited visibility | Fully transparent |
In conclusion, smart contracts are poised to revolutionize the way digital agreements are formed and executed. With the convergence of advanced technologies and a growing understanding of blockchain, the future of smart contracts is bright. As businesses continue to explore their applications, the potential for efficiency, security, and innovation is boundless.









